(Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2014, 53, 5624-5628)
固体核磁共振(Solid-state NMR)是在类天然环境的磷脂膜中研究膜蛋白的强力工具。我们采用三维魔角旋转(Magic angle spinning, MAS)固体核磁共振技术,对重组于大肠杆菌(E. coli)膜的二酯酰甘油激酶(Diacylglycerol kinase, DAGK)进行了结构分析。研究发现:DAGK在E. coli膜中的二级结构和拓扑结构与液体NMR(去垢剂DPC环境)以及X-ray晶体学(脂质立方相环境)研究得到的结果存在差别。本研究为“膜环境影响膜蛋白结构”提供了有力的例证。
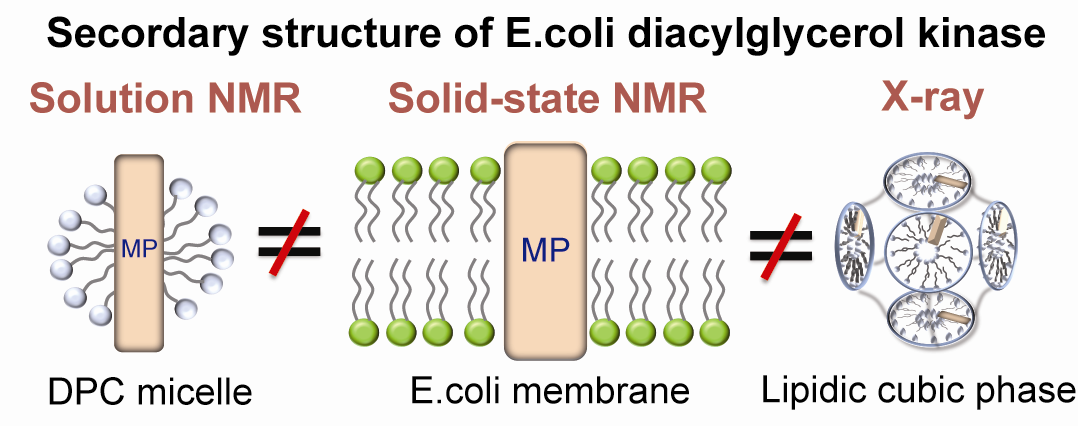
Conformation and Topology of Diacylglycerol Kinase in E.coli Membranes Revealed by Solid-state NMR Spectroscopy
Abstract Solid-state NMR is a powerful tool for studying membrane proteins in a native-like lipid environment. 3D magic angle spinning (MAS) NMR was employed to characterize the structure of E.coli diacylglycerol kinase (DAGK) reconstituted into its native E.coli lipid membranes. The secondary structure and topology of DAGK revealed by solid-state NMR are different from those determined by solution-state NMR and X-ray crystallography. This study provides a good example for demonstrating the influence of membrane environments on the structure of membrane proteins.


